Program 4.3 (Energy) comprises a single project (Project 4.31) focused on the spatial information priorities of electricity distribution companies, in particular Ergon Energy. Aerial inspection of large powerline networks by low altitude fixed-wing aircraft is a complex and potentially hazardous task.
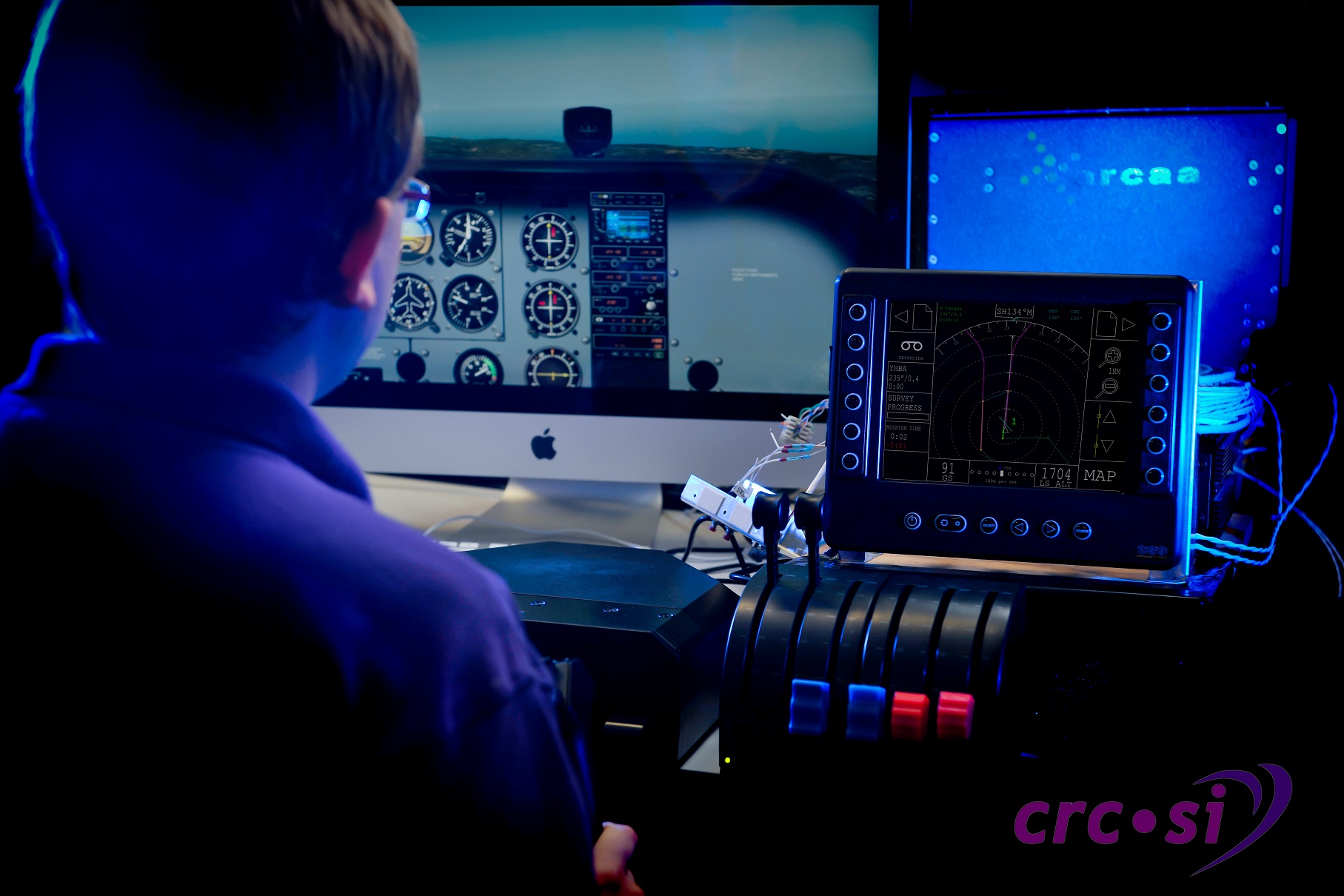
This motivates investigation of new aircraft planning and control technologies to improve the safety and efficiency of powerline inspection. Since 2009, the CRCSI has researched and developed flight-test-proven automated aerial powerline inspection technologies. The enhanced Flight Assist System (eFAS) project aims to extend the 2D aircraft flight-path planning, data capture and flight assist concepts developed under previous CRCSI projects to an active 3D capability.
The benefits are:
- reduced pilot workload regarding the horizontal and vertical control of the aircraft, maintenance of safe horizontal and vertical separation from terrain / obstacles, and positioning the aircraft at the correct altitude and speed
- consistent data capture
- reduced flight mission times and improved operational efficiencies.
The research team developed a system that delivers substantial efficiency gains applicable to hundreds of thousands of kilometres of powerline assets.
End user engagement in the Program is very strong and research outputs find direct application in Ergon’s ROAMES system. ROAMES is an outcome of Ergon’s engagement in CRCSI-1 and is operational. To date, the ROAMES aircraft have flown a total of 240,000 km under Flight Assist System (FAS) control, of which 75,000 km has been in inspection mode.
This equates to surveying approximately 55,000 km of Ergon’s 150,000 km of powerline network, with the target of surveying the complete network in a year.
Efforts to engage other energy companies in the research are ongoing, but managing commercial sensitivities are an important consideration governing the pace of commercialisation. In 2013, Ergon exercised an Australian and global license on the FAS background IP.